
Framing for teaching plumbing involves embedding work ready, world ready, and future ready skills. This approach makes training more holistic. It aligns with what employers, communities, and the industry need. The items below are a first draft. They show how we in the plumbing department are viewing this ethos. This perspective is being used across college.
1. Work Ready
(Practical skills and attitudes to start a plumbing job effectively)
- Technical mastery: Emphasize hands-on training with tools, fixtures, and materials commonly used in industry. Include troubleshooting tasks that mirror real job-site challenges.
- Safety-first mindset: Integrate HASAW/HSE practices into every lesson (e.g., personal protective equipment, confined spaces, handling pressurized systems).
- Jobsite professionalism: Build in role-play around client communication, punctuality, and site etiquette.
- Documentation skills: Teach students how to read and produce work orders, quotes, and compliance paperwork.
- Mock workplace environments: Simulate job sites in class where students have to plan, install, and test systems under time constraints.
2. World Ready
(Being able to contribute as responsible, adaptable citizens beyond just plumbing)
- Environmental awareness: Teach water conservation practices, greywater recycling, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient plumbing systems.
- Sustainability focus: Discuss global water challenges and how plumbers contribute to solutions (e.g., reducing wastage, safe sanitation).
- Teamwork & communication: Integrate group projects and cross-trade collaboration with electricians, builders, etc.
- Cultural awareness: Bring in examples of plumbing practices across the world and how solutions vary depending on community needs.
- Ethics & compliance: Emphasize integrity in quoting, using safe materials, and following regulations.
3. Future Ready
(Prepared for industry changes, technology, and lifelong learning)
- Digital tools: Introduce software for design, job management, and digital compliance reporting.
- Smart plumbing systems: Explore emerging tech such as water meters, leak detection sensors, and automated fixtures.
- Green technology integration: Cover solar hot water, hydrogen-ready systems, and other low-carbon innovations.
- Adaptability: Foster a mindset of upskilling—encouraging students to see themselves as lifelong learners in a changing industry.
- Entrepreneurial skills: Teach business basics—quoting, marketing, customer relations—so they can grow into self-employment or management roles.

One way to bring this together is by designing modules or projects. In these projects, students must solve a plumbing scenario. This scenario should touch all three dimensions. For example:
- Scenario: A client wants an energy-efficient home plumbing system.
- Work Ready: Students install and test the piping and fixtures.
- World Ready: They explain water-saving benefits to the client and consider environmental impacts.
- Future Ready: They integrate a smart water monitoring system. They reflect on how tech will shape plumbing in the next 10 years.



Topic Focus
Installation, commissioning, and client communication for a hot water system.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Install and test a domestic hot water system safely and according to standards. (Work Ready)
- Explain the environmental and social impacts of different hot water systems. (World Ready)
- Explore new technologies and trends shaping the future of hot water delivery. (Future Ready)
Lesson Stages
1. Introduction (15 min)
- Quick discussion: “Where do we see hot water in daily life? What would life look like without it?”
- Link to employability: “Clients rely on plumbers not just to install, but to advise on the best long-term, sustainable solutions.”
2. Work Ready Component (Hands-on Skills) (60 min)
- Demonstration & Practice:
- Assessment Activity: Students complete a live install in pairs, using checklists like those used by plumbing inspectors.
3. World Ready Component (Discussion + Reflection) (30 min)
- Class discussion:
- Compare gas, electric, solar, and heat-pump systems.
- Environmental impact: emissions, water conservation, and recycling opportunities.
- Social impact: equity of access — how remote/low-income communities may struggle with certain systems.
Mini-task: Students prepare a “client explanation” role-play. They practice advising a customer on choosing the most sustainable and cost-effective option.
4. Future Ready Component (Exploration + Critical Thinking) (30 min)
- Showcase & Discussion:
- Activity: Groups brainstorm “The hot water system of 2040.” They consider what it might look like. They also discuss what skills a plumber will need to install and maintain it.
5. Wrap-Up & Assessment (15 min)
- Students complete a reflection sheet:
- Work Ready: What technical skill did you strengthen today?
- World Ready: How does plumbing connect to environmental or social issues?
- Future Ready: What technology or trend excites you most, and why?
Assessment Methods
- Practical installation checklist (skills-based).
- Role-play client conversation (communication & ethics).
- Group presentation on “Future Hot Water Systems” (innovation & adaptability).
Extension Idea
Take students on a site visit (or virtual tour) to see solar hot water or smart plumbing systems in action. This will reinforce the world ready and future ready connections.
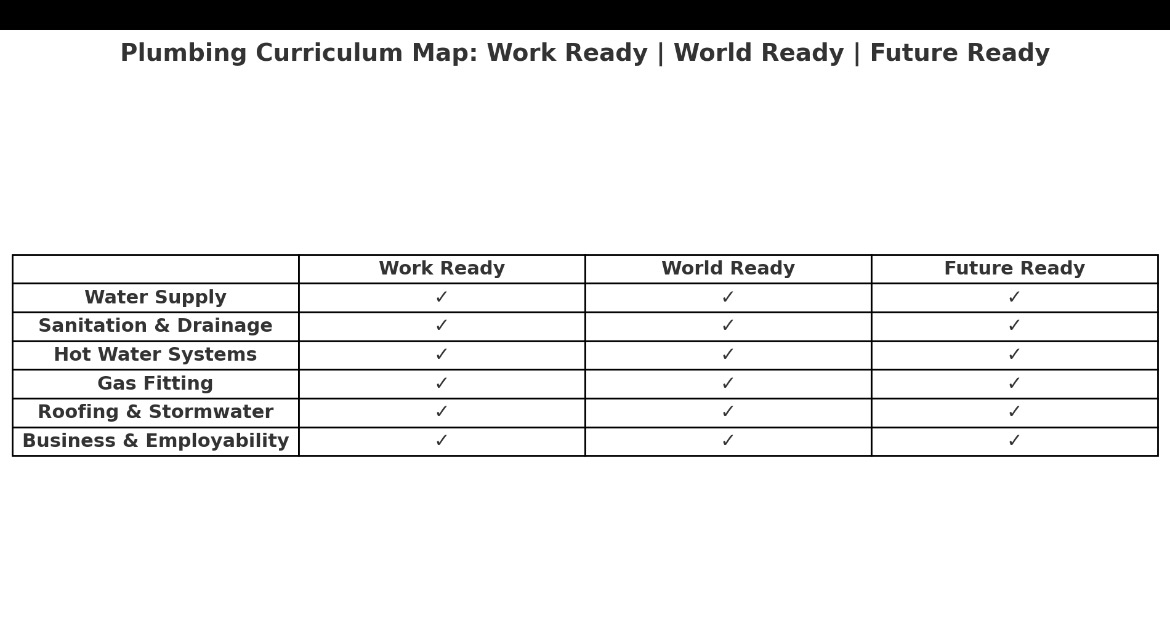
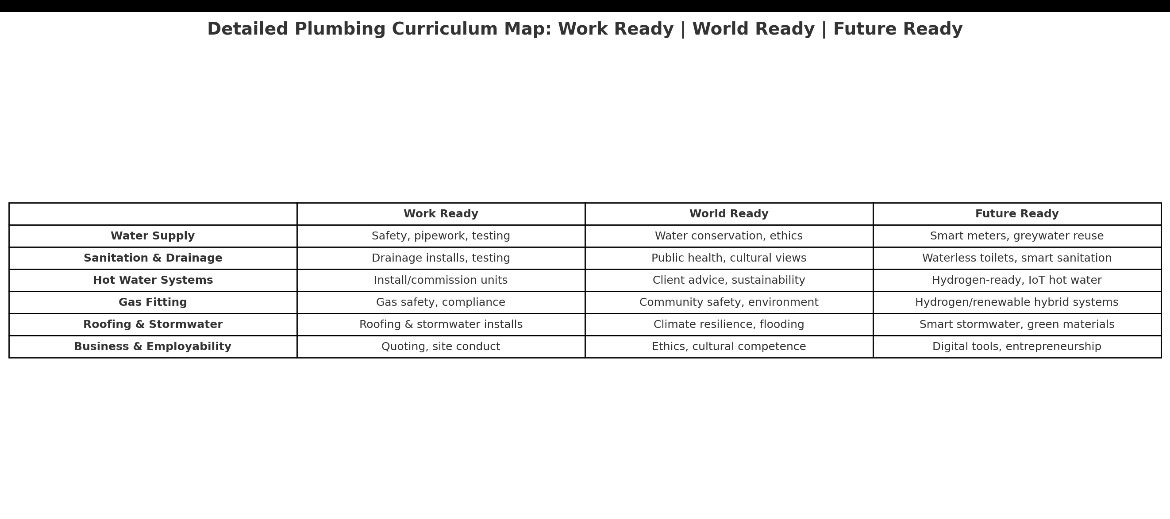
Plumbing that embeds Work Ready, World Ready, and Future Ready across the main areas of the trade. Instead of just one-off lessons, this offers a series of modules, each with suggested learning activities and assessments.

Plumbing Teaching Framework
1. Water Supply Systems
- Work Ready
- Pipe sizing, installation, joining techniques.
- Reading and interpreting schematics.
- Safety (pressure testing, backflow prevention).
- World Ready
- Water scarcity and conservation.
- Ethical responsibility in ensuring safe drinking water.
- Case study: comparing water supply challenges in different regions.
- Future Ready
- Smart metering and leak detection systems.
- Greywater reuse systems.
- Future global water challenges and technological responses.
2. Sanitation & Drainage
- Work Ready
- Installing soil and waste systems.
- Testing and commissioning drainage lines.
- Following health and safety codes.
- World Ready
- Public health impacts of effective sanitation.
- Cultural practices in sanitation across the world.
- The plumber’s role in disease prevention.
- Future Ready
- Innovations in waste-to-energy systems.
- Waterless toilets and low-water designs.
- Urban planning and smart city sanitation solutions.
3. Hot Water Systems
(from the earlier detailed lesson)
- Work Ready: Install and commission hot water units.
- World Ready: Advise clients on sustainable choices.
- Future Ready: Explore hydrogen-ready, solar, and IoT-integrated systems.
- Work Ready
- Safe installation and testing of gas appliances.
- Compliance with standards and safety codes.
- Risk management with leaks and combustion testing.
- World Ready
- Environmental considerations of gas use.
- Public safety awareness — plumber as a community protector.
- Future Ready
- Hydrogen-ready appliances.
- Transition to low-emission fuels.
- Integration of gas and renewable hybrid systems.
5. Rainwater & Drainage
- Work Ready
- Installing gutters, downpipes, and stormwater drains.
- Safety working at heights.
- Maintenance and repair techniques.
- World Ready
- Flood prevention and resilience in communities.
- Designing for extreme weather and climate change.
- Future Ready
- Smart stormwater management systems.
- Materials innovation (self-cleaning, recycled).
- Integration into green buildings and sustainable cities.
6. Business & Employability Skills
- Work Ready
- Quoting, invoicing, scheduling jobs.
- Customer communication.
- Professional conduct on site.
- World Ready
- Ethics in pricing and compliance.
- Building trust with clients and communities.
- Cultural competence in diverse workplaces.
- Future Ready
- Running a digital plumbing business (apps, job management software).
- Entrepreneurship opportunities (eco-plumbing, niche markets).
- Lifelong learning and adapting to industry disruption.
How This Works in Practice
- Each module includes technical (Work Ready), social/environmental (World Ready), and innovation/technology (Future Ready) components.
- Assessment structure could mix:
- Practical installs (Work Ready).
- Reflection journals or client role-plays (World Ready).
- Innovation projects or presentations (Future Ready).

As mentioned earlier in this article, this is a work in progress. I look forward to meeting with others within the college to broaden the content. I also aim to share ideas with my peers to benefit all students at Bolton College.



Leave a comment