Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) are a type of heat pump that uses the outside air as a heat source. They can be used to heat and cool homes and businesses. To design an air source heat pump system, you will need to consider the following factors:
- The size of the space to be heated or cooled
- The climate in the area
- The efficiency of the heat pump
- The budget for the project
Once you have considered these factors, you can begin to design the system. The main components of an air source heat pump system are the compressor, the evaporator, the condenser, and the expansion valve. The compressor is the heart of the system. It uses electricity to compress the refrigerant, which then flows through the evaporator. The evaporator is located in the conditioned space. It absorbs heat from the air and transfers it to the refrigerant. The condenser is located outside the conditioned space. It rejects heat from the refrigerant to the outside air. The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant through the system.
After the system is designed, it is installed. The installation process involves connecting the components of the system and ensuring that they are properly sealed. The system is then tested to make sure that it is working properly.
Air source heat pumps are a great option for heating and cooling homes and businesses. They are energy efficient, environmentally friendly, and relatively easy to maintain. If you are considering installing an air source heat pump system, be sure to consult with a qualified professional.

A compressor is a crucial component in a heat pump system, responsible for circulating refrigerant and driving the heat transfer process. It essentially acts as the heart of the heat pump, constantly pumping refrigerant through the system to absorb and release heat. The compressor’s primary function is to raise the pressure of the refrigerant, which significantly impacts its temperature. As pressure increases, the boiling point of the refrigerant also rises. This principle is essential for heat transfer in a heat pump.
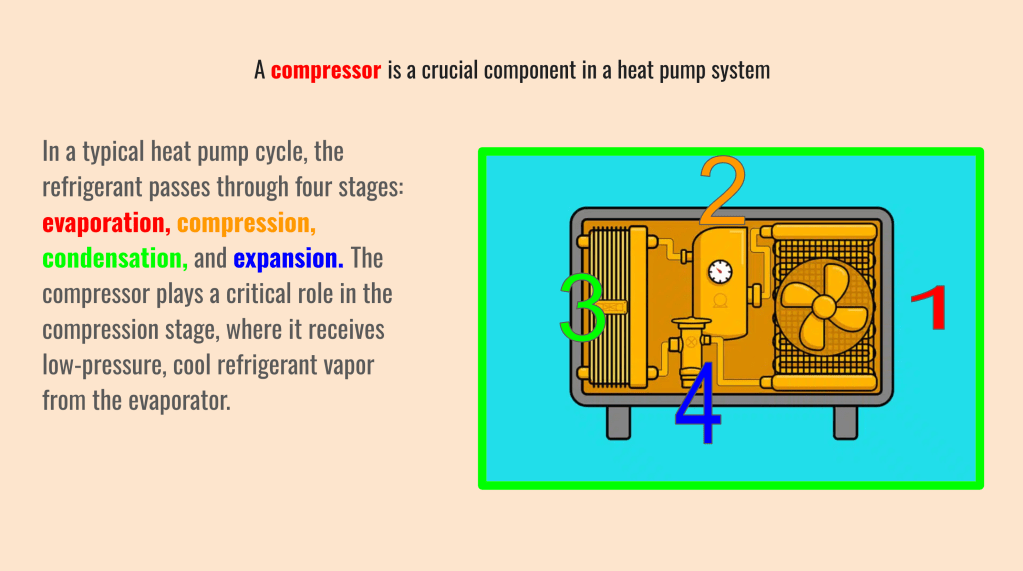
Inside the compressor, the refrigerant is subjected to mechanical compression, typically through a rotary or reciprocating mechanism. This compression elevates the refrigerant’s pressure and temperature, transforming it into a high-pressure, hot gas.
The high-pressure, hot refrigerant then enters the condenser, where it releases its heat to the surrounding environment. As the refrigerant loses heat, it condenses back into a liquid state. The condensed refrigerant, now at a high pressure and liquid state, passes through an expansion valve, where its pressure is abruptly reduced. This pressure drop causes the refrigerant to expand and vaporize, resulting in a significant drop in temperature.
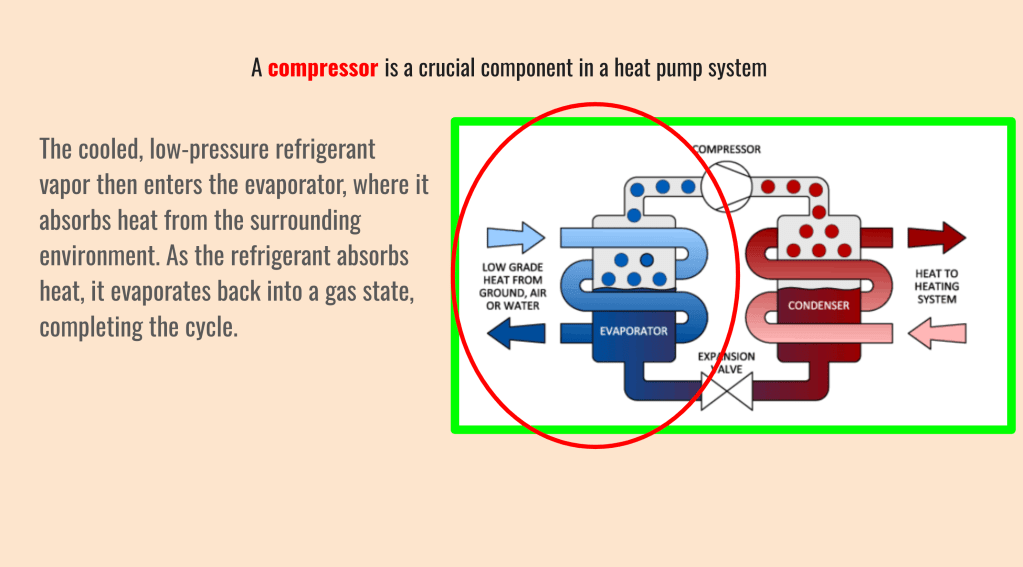
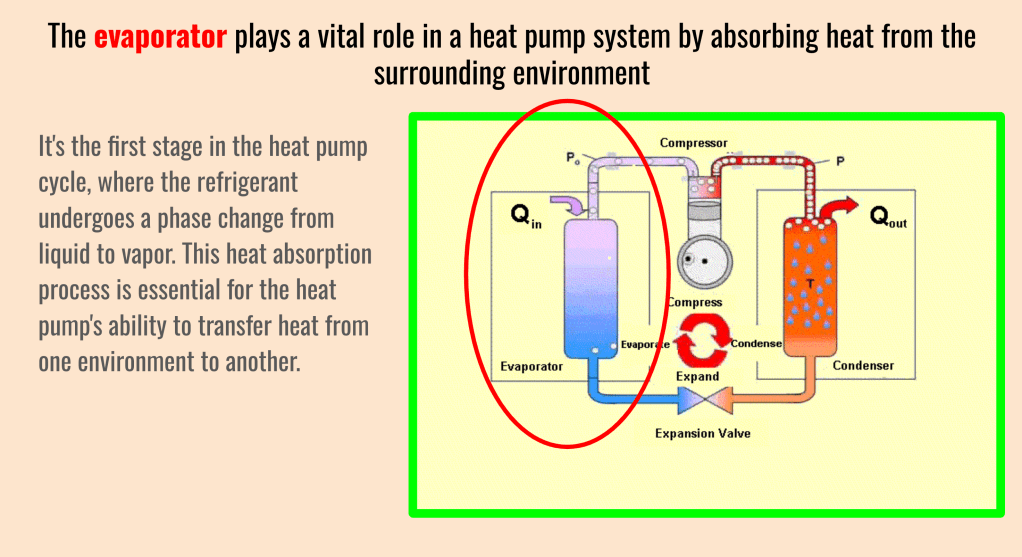
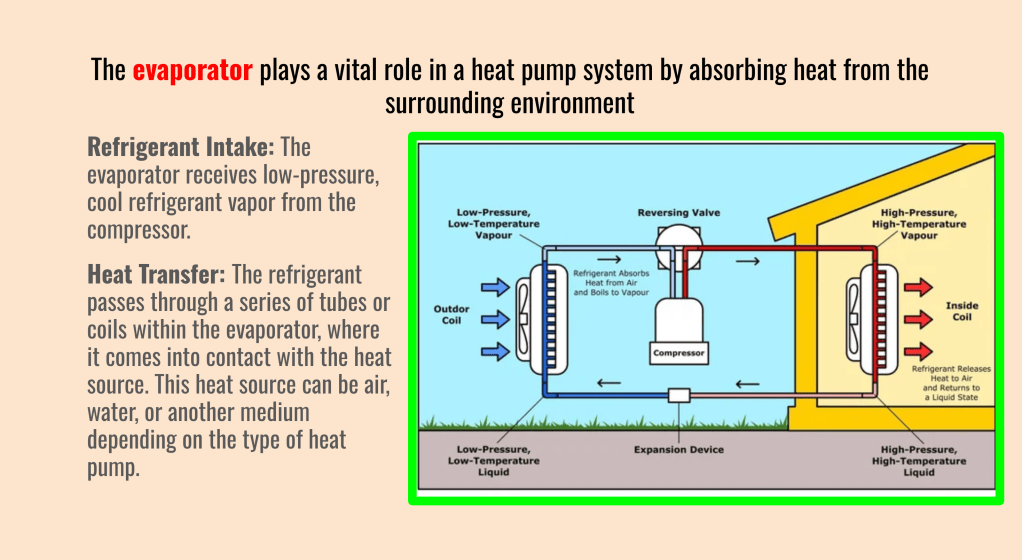
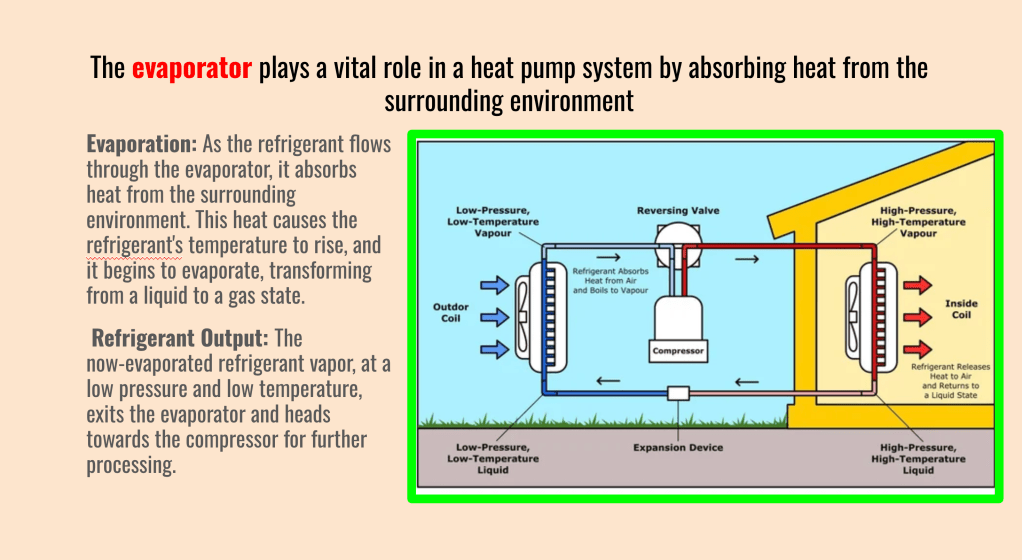
The evaporator is a fundamental component in a heat pump system, responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding environment. Its efficient operation is essential for the heat pump’s effectiveness in heating or cooling a space.
The Working Principle of the Condenser
Refrigerant Intake: The condenser receives high-pressure, hot refrigerant vapor from the compressor.
Heat Transfer: The refrigerant passes through a series of tubes or coils within the condenser, where it comes into contact with the heat sink. This heat sink can be air, water, or another medium depending on the type of heat pump.
Condensation: As the refrigerant flows through the condenser, it releases heat to the heat sink. This heat causes the refrigerant’s temperature to drop, and it begins to condense, transforming from a gas to a liquid state.Refrigerant Output: The now-condensed refrigerant liquid, at a high pressure and high temperature, exits the condenser and heads towards the expansion valve for further processing.
The condenser is a fundamental component in a heat pump system, responsible for releasing heat to the surrounding environment. Its efficient operation is essential for the heat pump’s effectiveness in heating or cooling a space.
An expansion valve is a critical component in a heat pump system. It regulates the flow of refrigerant through the system, which helps to control the temperature. The expansion valve is located between the condenser and the evaporator. As the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, its pressure drops and its temperature decreases. This allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the evaporator and transfer it to the condenser. The expansion valve is a vital part of the heat pump system, and it helps to ensure that the system operates efficiently. Without an expansion valve, the heat pump would not be able to function properly.



Leave a comment